Table Of Content

A non‐randomized clinical trial involves an approach to selecting controls without randomization. With this type of study design a pattern is usually adopted, such as, selection of subjects and controls on certain days of the week. Depending on the approach adopted, the selection of subjects becomes predictable and therefore, there is bias with regards to selection of subjects and controls that would question the validity of the results obtained. Linda M. Crawford, professor emerita at Walden University, received her doctoral degree from the University of Minnesota with emphases in curriculum and educational administration. She also advised institutions extensively on the faculty perspective related to academic initiatives, including development of new faculty orientation programs, faculty governance, and faculty models. Prior to her work in quality assurance, Linda held both teaching and administrative positions at all levels of education, including P-12, undergraduate, and graduate education.
Reliability and validity
The Scientific Method Steps, Uses, and Key Terms - Verywell Mind
The Scientific Method Steps, Uses, and Key Terms.
Posted: Tue, 28 Feb 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
The selection of a specific research design method should align with the research objectives, the type of data needed, available resources, ethical considerations, and the overall research approach. Researchers often choose methods that best suit the nature of their study and research questions to ensure that they collect relevant and valid data. For example, a case study may involve different methods of data collection such as survey, interviews, observations, analysis of documents, etc.
Frequently asked questions about surveys
Rates of maternal and infant morbidity and mortality in the United States far exceed those of comparable nations [1]. The burdens of racist policies have produced vastly worse outcomes for Black and Native, relative to White, populations [2]. For example, Black and Native birthing people are more than three times as likely to experience pregnancy-related mortality compared to white birthing people [3]. These racial inequities are not adequately explained by individual behaviors or other socio-economic factors, but are a complex intersection of factors shaped by structural and social determinants [2, 6], policies and institutions carrying out such policies [7]. There is a long history of structural racism that has resulted in practices and policies that have had a detrimental impact on Black and Indigenous populations in the United States [8]. Findings from this study are expected to advance knowledge about how Medicaid programs can best implement policy interventions to promote racial equity in pregnancy and early childhood health.
Sampling methods
We’ll carefully manage any future changes to courses, or the support and other services available to you, if these are necessary because of things like changes to government health and safety advice, or any changes to the law. Any annual increase in tuition fees as provided for above will be notified to students at the earliest opportunity in advance of the academic year to which any applicable inflationary rise may apply. That's usually an IELTS 6.0 qualification (with a minimum of 5.5 in all sections). We welcome applications from mature candidates, including those without formal qualifications, provided you can demonstrate relevant experience and ability. We have also reduced the costs of studying with free laptop loans, free learning resources and discounts to save money on everyday things.
Prospective versus retrospective study designs
Some popular examples of positivist designs include laboratory experiments, field experiments, field surveys, secondary data analysis, and case research, while examples of interpretive designs include case research, phenomenology, and ethnography. Note that case research can be used for theory building or theory testing, though not at the same time. Some techniques such as focus groups are best suited for exploratory research, others such as ethnography are best for descriptive research, and still others such as laboratory experiments are ideal for explanatory research. Interest from policymakers in payment reforms to improve health equity has increased recently; however, information on the implementation and effects of such models is sparse [48, 49].
Careers
Interventional studies are experiments where the researcher actively performs an intervention in some or all members of a group of participants. This intervention could take many forms – for example, administration of a drug or vaccine, performance of a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure, and introduction of an educational tool. For example, a study could randomly assign persons to receive aspirin or placebo for a specific duration and assess the effect on the risk of developing cerebrovascular events.
Step 3: Identify your population and sampling method
For Aim 1, outcomes include binary measures of initiating prenatal care in the first trimester, and children receiving at least 6 well-child visits in the first six months of life. We will compare outcomes among Black beneficiaries relative to those of other racial groups, post- relative to pre- implementation of the equity incentive payment program. Cohort studies are study designs that compare two groups, such as the subjects with exposure/risk factor to the subjects without exposure/risk factor, for differences in incidence of outcome/disease. Most often, cohort study designs are used to study outcome(s) from a single exposure/risk factor. Thus, cohort studies can also be hypothesis testing studies and can infer and interpret a causal relationship between an exposure and a proposed outcome, but cannot establish it (Figure 4).
Typically, most cohort studies are prospective studies (though there may be retrospective cohorts), whereas case–control studies are retrospective studies. An interventional study has to be, by definition, a prospective study since the investigator determines the exposure for each study participant and then follows them to observe outcomes. Based on the direction of inquiry, study designs may be classified as forward-direction or backward-direction. In forward-direction studies, the researcher starts with determining the exposure to a risk factor and then assesses whether the outcome occurs at a future time point. For example, a researcher can follow a group of smokers and a group of nonsmokers to determine the incidence of lung cancer in each. In backward-direction studies, the researcher begins by determining whether the outcome is present (cases vs. noncases [also called controls]) and then traces the presence of prior exposure to a risk factor.
They allow you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem. For practical reasons, many studies use non-probability sampling, but it’s important to be aware of the limitations and carefully consider potential biases. You should always make an effort to gather a sample that’s as representative as possible of the population. This approach is about gaining a rich, detailed understanding of a specific context or phenomenon, and you can often be more creative and flexible in designing your research. Any change in test scores could have been influenced by many other variables, such as increased stress and health issues among students and teachers.
Field surveys are non-experimental designs that do not control for or manipulate independent variables or treatments, but measure these variables and test their effects using statistical methods. Field surveys capture snapshots of practices, beliefs, or situations from a random sample of subjects in field settings through a survey questionnaire or less frequently, through a structured interview. The strengths of field surveys are their external validity (since data is collected in field settings), their ability to capture and control for a large number of variables, and their ability to study a problem from multiple perspectives or using multiple theories. More complex designs may include multiple treatment groups, such as low versus high dosage of the drug or combining drug administration with dietary interventions.
It is particularly helpful in terms of developing predictions, and given that it doesn’t involve the manipulation of variables, it can be implemented at a large scale more easily than experimental designs (which will look at next). Experimental and quasi-experimental designs allow you to test cause-and-effect relationships, while descriptive and correlational designs allow you to measure variables and describe relationships between them. It’s also possible to use a mixed methods design that integrates aspects of both approaches. By combining qualitative and quantitative insights, you can gain a more complete picture of the problem you’re studying and strengthen the credibility of your conclusions.
Experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This type of research design involves manipulating one variable and measuring the effect on another variable. It usually involves randomly assigning participants to groups and manipulating an independent variable to determine its effect on a dependent variable.
We have discussed various clinical research study designs in this comprehensive review. Though there are various designs available, one must consider various ethical aspects of the study. Hence, each study will require thorough review of the protocol by the institutional review board before approval and implementation. Some of the biases observed with cohort studies include selection bias and information bias.
Thus, the study design for prospective and retrospective cohort studies are similar as we are comparing populations with and without exposure/risk factor to development of outcome/disease. The policies under study involve modifying common Medicaid reimbursement arrangements– namely, pay-for-performance programs and maternity care bundled payments. The policies are modified to embed financial incentives for Medicaid health plans and healthcare providers to improve the quality of care and health outcomes for Black pregnant and parenting persons and their children. These are the first such payment policies, to our knowledge, that explicitly aim to promote racial health equity with an explicit focus on addressing inequities that affect Black and Indigenous populations in Pennsylvania.
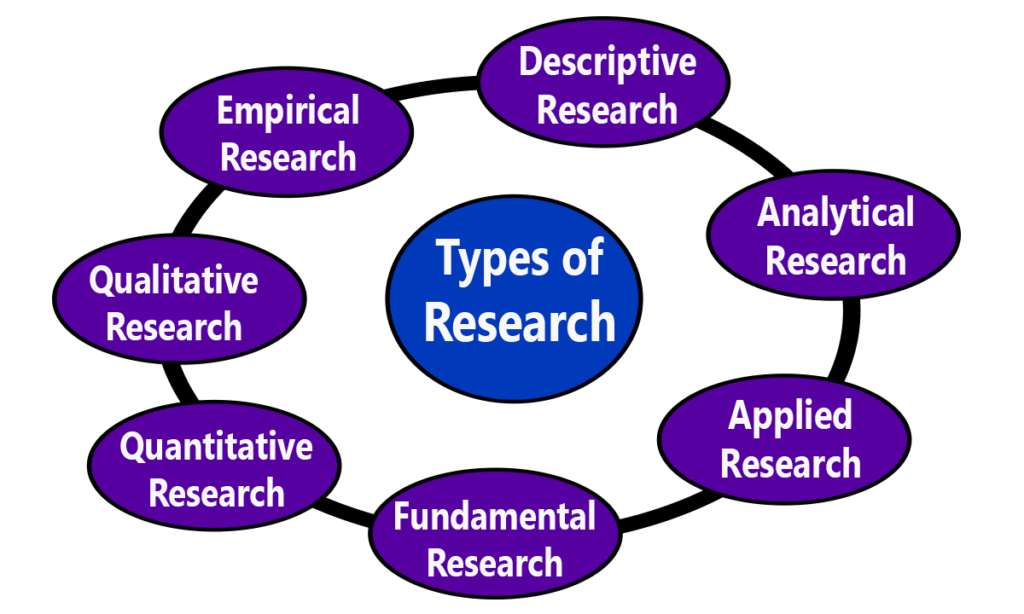
There are various research designs, such as experimental, observational, survey, case study, and longitudinal designs, each suited to different research questions and objectives. The choice of research design depends on the nature of the research and the goals of the study. Research methods and research design are terms you must know before starting a research project. However, many new researchers assume research methods and research design to be the same. For example, if you are building a house, you need to have a good idea about what kind of house you are going to build; you cannot do anything without knowing this.

No comments:
Post a Comment